Resources
Browse resources created and collated by ARIIA as a trusted, evidence-based guide to supporting innovation across the aged care sector.
Showing
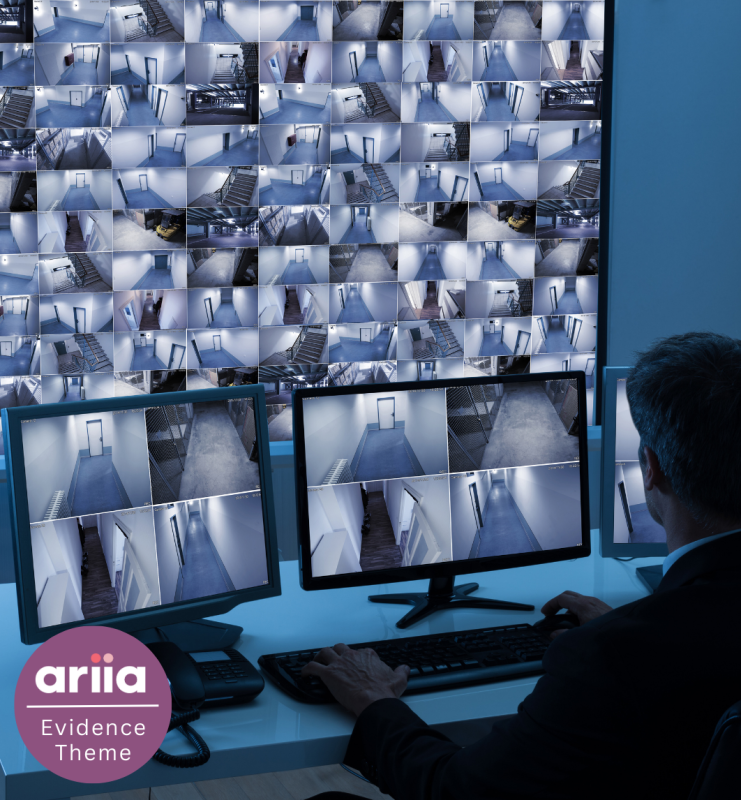

Technology in aged care: Privacy and safety
Some technologies used in aged care settings raise privacy concerns for older people, their families, aged care staff, and providers. This resource from ARIIA is a short easy-to-read summary of the research evidence.

Technology in aged care: Implementing technology
There can be no one-size-fits-all approach to successful implementation due to the relationships between the technical, human, and organisational factors in complex care settings such as aged care. This resource from ARIIA is a short easy-to-read summary of the research evidence.

Technology in aged care: Creating a business case
The information gained from a careful technology needs assessment can be used to write a business case for purchasing technology. A business case is an important part of project documentatio. This resource from ARIIA is a short easy-to-read summary of the research evidence.
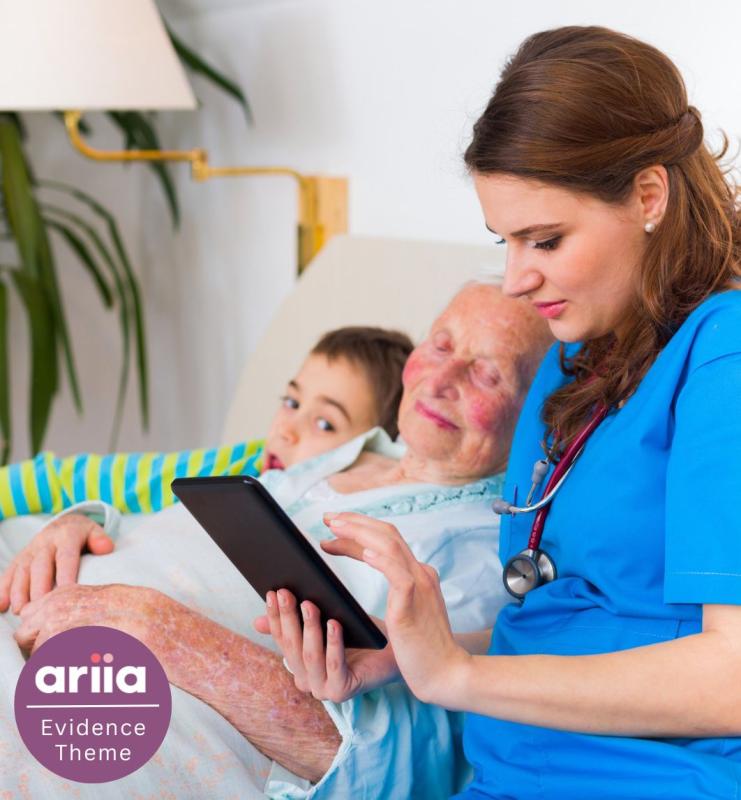

Technology in aged care: Monitoring use over time
Monitoring should be an ongoing process rather than a one-off event. By regularly monitoring technology use and making changes where indicated, organisations can improve the fit between technology assets and the context in which they are applied. This resource from ARIIA is a short easy-to-read summary of the research evidence.

Technology in aged care: Technology needs assessment
It is important that technologies deliver anticipated benefits by being fit for purpose. A needs assessment can lay the foundation for good decision-making, ensuring technology meets the needs of those who will be using it or affected by it. This resource from ARIIA is a short easy-to-read summary of the research evidence.

Technology in aged care: Cybersecurity concerns
With the increased uptake of technology in aged care services, cybersecurity has become a significant concern for service providers, aged care recipients, their family members, and care workers. This resource from ARIIA is a short easy-to-read summary of the research evidence.
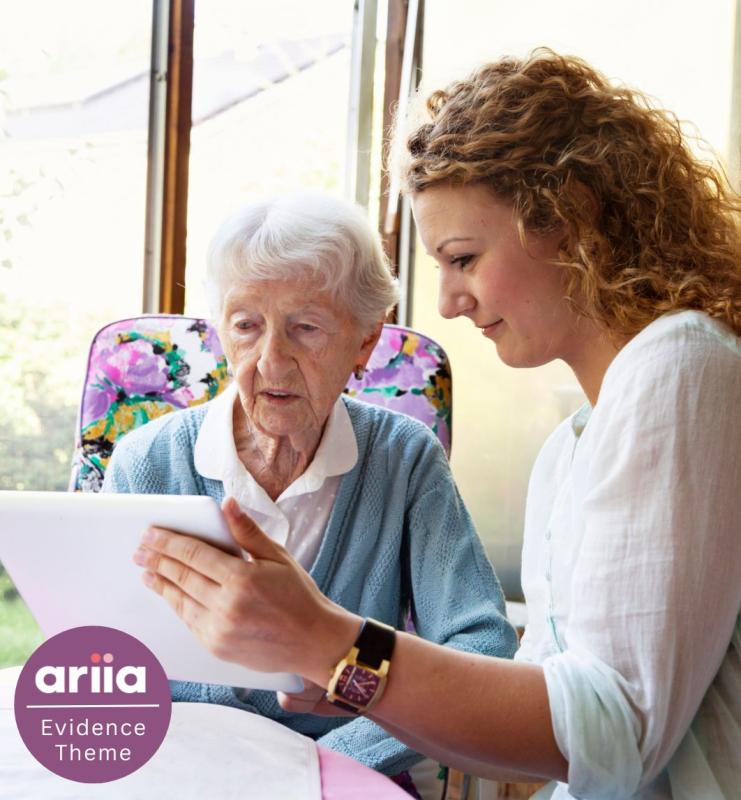

Technology in aged care: Quality of human interaction
Some people working in or receiving aged care services express concerns about certain forms of technology that may impact human-to-human interaction. This resource from ARIIA is a short easy-to-read summary of the research evidence.
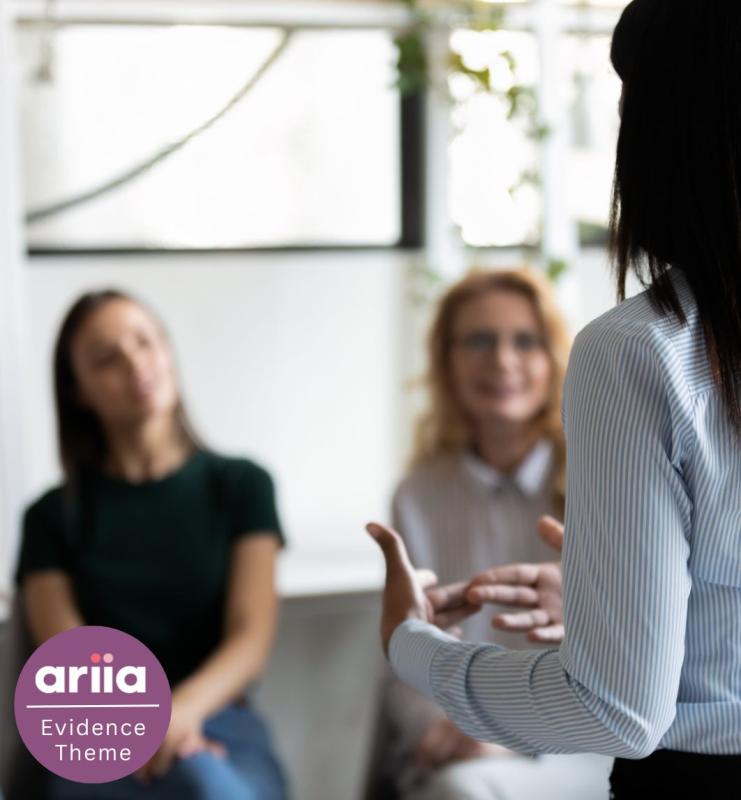

Technology in aged care: Staff technology training
With technological advancements, it is important that aged care staff have the knowledge and confidence to get the most out of workplace technology. This resource from ARIIA is a short easy-to-read summary of the research evidence.

Technology in aged care: Ethics and technology in aged care
Technology has the capacity to both limit and enhance autonomy for older adults. This resource from ARIIA is a short easy-to-read summary of the research evidence.
Technology in aged care: Attitudes towards robots
Robots can play a role in improving the wellbeing of older adults and provide opportunities for social and physical interactions. This resource from ARIIA is a short easy-to-read summary of the research evidence.